Product knowledge is one of the central components to successful selling. It is essential to have in-depth knowledge about the attributes of products in order to merchandise products together in a way that is logical and shopper-friendly.
Leading retailers increase their sales through proper merchandising and to do this they use planograms because they are one of the best ways to plan, communicate, implement and maintain your merchandising strategy.
1. Understand the basics
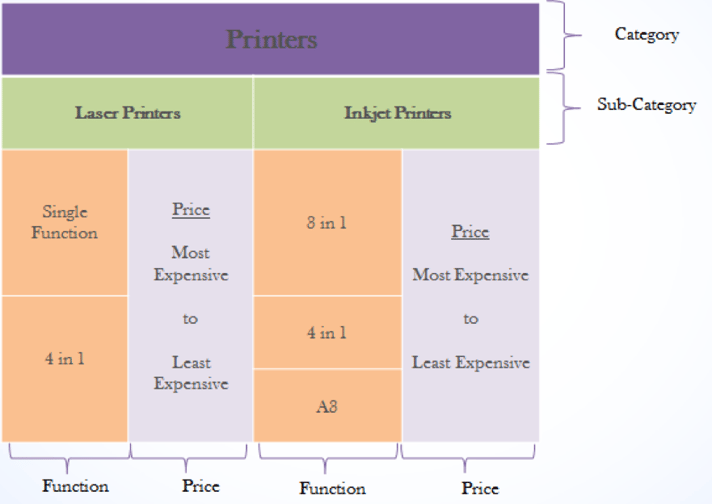
It is important for a space planner to understand the basic information about a product –its various functions, sizes, models and price points. In a category such as printers, one would need to know that there are laser printers and inkjet printers. Each of these sub-categories is available in different sizes and models that perform various functions.
For example, there is a single function printer available, which performs the basic print function, and there is a 4-in-1 function printer available, which performs scanning, faxing, printing, and copying functions. Without a basic knowledge of the products in the category, you're going to have a tough time creating a valuable plano.
2. Use your practical understanding to create a logical merchandising flow
Understanding the products in a category will enable you to merchandise the correct products in the correct product sequence within their sub-category.
Typically you would merchandise all laser printers together and all the inkjet printers together. Within each sub-category, the printers would be arranged by function and price. Merchandising this way allows consumers to easily compare the available product options and purchase the product that best satisfies their needs.
3. Combining tactical benefits of product knowledge with sales data
To create the best possible plano, a space planner needs to pair everything they know about a product with sales data for the category. This includes the monetary sales and the number of units sold over a specific period of time.
Sales history provides information about the product such as whether the product is seasonally purchased or frequently purchased. With sales data, retailers can identify an opportunity and choose to adopt a growth strategy for a particular sub-category or product.
This kind of information will suggest how many products or where the product should be merchandised on the shelf. For example, a consumer may choose to frequently upgrade their home or office printer to the latest model or a model that has more functions, whereas they will less frequently (perhaps seasonally) upgrade their large office A3 paper size printer.
4. Tactical product positioning and space allocation
Better product positioning is arranging the products in such a way as to drive sales. Product positioning is a flexible principle because the product’s position may change due to season or promotion, an increase or decrease in sales, or in order to support and drive the retailer’s strategy.
Space planners with good product knowledge will be able to create a neat shelf layout and a better visual appeal for the consumer, creating a positive shopping experience and generating better sales.
5. Understanding which products complement each other
You will often find products that complement each other merchandised fairly close to each other (cross-merchandising). This is convenient and logical for consumers. A space planner who knows which products complement each other will quickly identify them and merchandise them together in order to offer consumers a solution instead of a product.
An example of this would be: find printer models merchandised near the inks and toners.

By implementing planograms in stores, retailers will create a logical flow throughout a store assigning selling potential to every square metre. Merchandising can be improved with the use of planograms, for example, assisting staff with a better merchandising process and easier replenishment of sold products. Merchandising similar categories and sub-categories, within those categories, together make it easier for the consumer to shop.
Conclusion
With strong product knowledge, a space planner will know how to create the best possible planograms, prevent cluttered stores and manage shelf space to optimise sales. Combining real expertise and sales history, a planogram enables the right product to be merchandised at the right place in the right quantities.
This assists in driving sales and creating foot traffic, in turn generating revenue.


